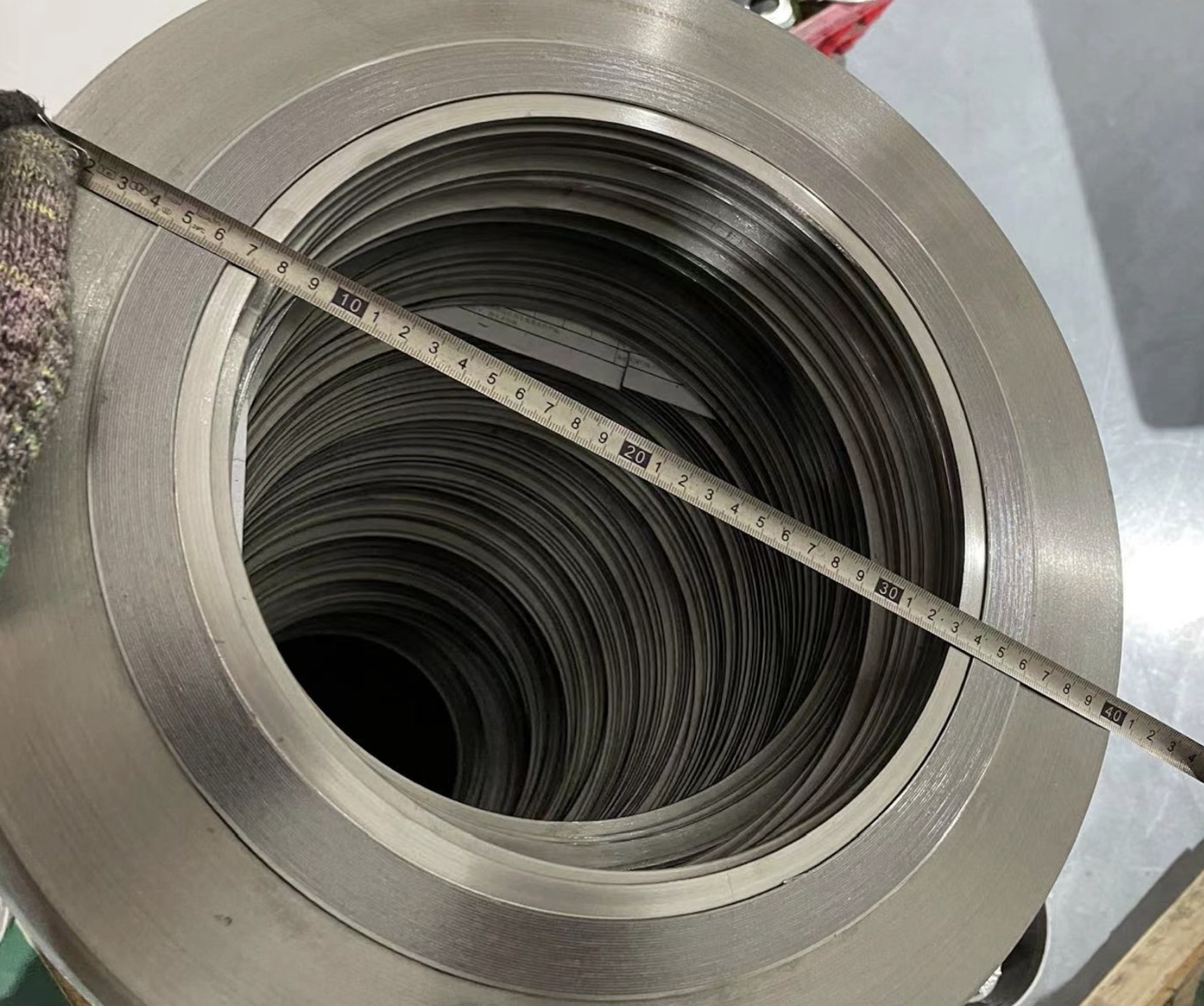
China Manufacturer of TSG SM05 316L/GRAF 316L-IR ASME B16.20 24″ 300# SWG with inner and outer guide ring
What is TSG SPIRAL WOUND GASKETS?
The sealing element of the spiral wound gasket consists of a v-shaped metal strip spirally wound in combination with a soft sealing material filler. The metal strip provides outstanding resilience, while the flexible sealing filler guarantees excellent sealing. Due to this combination of materials the spiral wound gasket is suitable for sealing under severely fluctuating temperature and pressure conditions. Depending on the application the spiral wound gasket can be specified with outer and/or inner rings
Characteristics
The spiral wound gasket is suitable for use across a wide pressure range and is therefore virtually applicable. • The spiral wound gasket can be used to seal fluid pressures up to 250 bar and damage (although extra care should be taken during transportation and installation of large diameter gasket without guide rings). • The outer guide ring serves to locate the spiral element centrally on the flange faces and prevent blow-out. • By combining different winding materials and metals the gasket can be tailored to a wide variety of operating conditions. • Due to its non-adhesive character the gasket is easy to remove after service. • The gasket does not cause damage to the flange faces
Benefits of the centring ring
The spiral wound gasket outer centring ring provides the following benefits:
• Optimum location between the bolts.
• Protection of the spiral wound element.
• Additional security against gasket blow-out.
• Acts as compression limiter preventing overloading and overcompression of the spiral wound element.
• Prevents radial-flow of soft fillers, such as P.T.F.E. For these reasons it is preferable to use spiral wound gasket with outer centring rings. The the outer ring is marked with nominal size, pressure class, standard and materials.
Benefits of the inner ring
The spiral gasket inner ring provides the following benefits:
• Prevents radial-flow of soft fillers, such as P.T.F.E.
• Reduces turbulence-minimising flow resistance and crevice corrosion.
• Acts as a heat shield when the spiral wound gasket is subjected to high temperatures.
• Avoidance of over-compression at elevated seating loads in high-pressure service
• Improvement of the load distribution over the gasket Inner and outer rings are particularly recommended for use on spiral wound askets exceeding class 600lbs, but specifically recommended for high temperatures and Pressures to optimise the operational reliability of the spiral wound sealing element.
Material selected for the inner ring and winding metal is usually the same as the flange metal, in order to prevent corrosion and differential expansion problems. The outer centring ring is generally manufactured from carbon steel with an anti-corrosion treatment, however the ring may also be manufactured in the same metal as the flange to prevent corrosion.
TSG SM05 SWG with inner and outer guide ring This style offers the best performance for raised-face flange connections
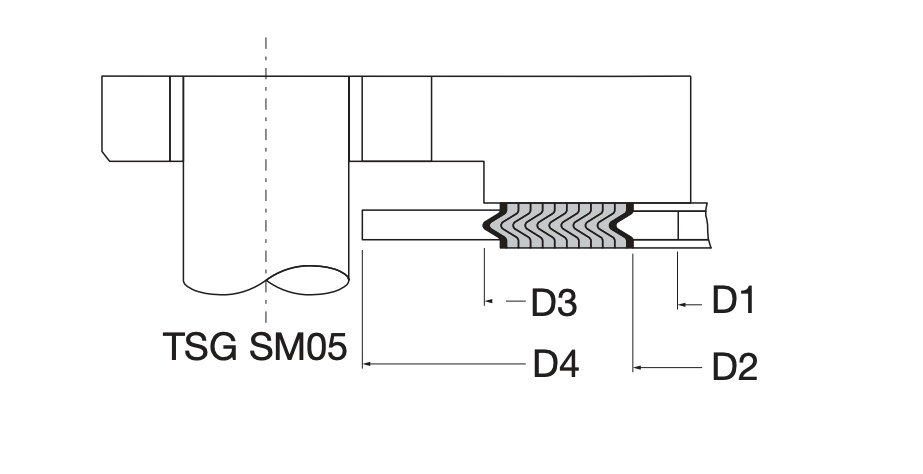
inner and outer guide ring materials for SPIRAL WOUND GASKETS
Standard fillers material for SPIRAL WOUND GASKETS
Graphite is universally applicable, high-quality, asbestos-free material with a very good chemical resistance, resistance to ageing, good gastightness. PTFE is a high quality synthetic material with an excellent chemical resistance, resistance to temperature up to 250oC, resistant to ageing, excellent gastightness. Non standard materials are available on request.
Spiral Wound Gasket (SWG) size standards are typically defined by international standards organizations, such as ASME, API, EN, or JIS.
Standards Governing SWG Dimensions
- ASME B16.20:
- Covers gaskets for use with flanges per ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.47.
- Specifies dimensions, tolerances, materials, and marking for spiral wound gaskets.
- EN 1514-2:
- Governs the dimensions of SWGs for use with EN flanges.
- JIS B2404:
- Covers Japanese Industrial Standards for gasket dimensions, including SWGs.
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): Matches the flange size the gasket is designed to fit.
- Pressure Class: The rating (e.g., Class 150, 300, 600, etc.) indicates the maximum working pressure.
- Gasket Dimensions:
- Inner Diameter (ID): Matches the bore of the flange to avoid gasket overhang.
- Outer Diameter (OD): Fits within the flange bolts.
- Thickness: Standard thickness is often 3.2 mm (1/8 inch) or 4.5 mm (3/16 inch), though other options exist.
Typical Size Ranges
- Nominal Pipe Sizes (NPS): 1/2″ to 60″ (or larger for custom applications).
- Pressure Classes:
- ASME: Class 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500.
- DIN/EN: PN10, PN16, PN25, PN40, etc.

