ASTM A453 Grade 660 Cl A B C D Stud Bolt
Professional manufacturer of ASTM A453 GR.660- A-B-C-D- Studs Bolt & A453 GR.660 Nuts in China
ASTM A453 Grade 660 is a high-strength, corrosion-resistant, precipitation-hardening stainless steel alloy designed for use in high-temperature applications. This material is commonly used for bolts, studs, and other fasteners in environments that demand superior mechanical properties and stability under thermal and stress conditions.
ASTM A453 Grade 660 stud bolts are high-strength, corrosion-resistant fasteners widely used in high-temperature environments. This specification covers bolts, studs, and other components made from precipitation-hardening stainless steel. The Grade 660 material is divided into four classes (A, B, C, D) based on mechanical properties and heat treatment
ASTM A453 Grade 660 is also known as A286 is an iron-based, nickel containing superalloy
ASTM A453/A453
Standard Specification for High-Temperature Bolting, with Expansion Coefficients Comparable to Austenitic Stainless Steels
This specification covers standards for Grade 660 (Class A, B, C, and D) , Grade 651 (Class A and B), Grade 662 (Class A and B), and Grade 665 (Class A and B) of bolting materials for use in high-temperature service such as fasteners, for pressure vessels and valve flanges. Bolting materials in this specification covers rolled, forged, or hot-extruded bars, and also bolts, nuts, screws, washers, studs, and stud bolts. Materials shall adhere to specified contents of carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, tungsten, titanium, columbium, aluminum, vanadium, boron, and copper. Materials shall be subjected to tension, stress-rupture, and hardness tests. Materials shall conform to yield strength, tensile strength, elongation, reduction of area, Brinell hardness, and Rockwell hardness requirements. Hardening and solution treatment requirements for each material class are also given.
(UNS S66286)
– A-286 Alloy
A precipitation hardening stainless steel, NAS 660 (SUH 660, UNS S66286) maintains superior strength at high temperatures up to 700℃, surpassing austenitic stainless steels. With a higher nickel content than Type 304, NAS 660 also includes such elements as titanium and aluminum for hardening. Age hardening is used to precipitate γ’ phase [Ni3 (Al, Ti)] making this an extraordinarily strong metal at high temperatures.
X6NICRTIMOVB25-15-2, 1.4980, 1.3980, 1.4606, 1.4944, A-286, GRADE 660 STEEL – SPECIAL HEAT-RESISTANT AUSTENITIC CHROMIUM-NICKEL STEEL WITH CARBIDE-FORMING ELEMENTS ACCORDING TO PN-EN 10302, PN-EN 10088-1 AND PN-EN 10269.
ASTM A453-Grade 660 Stud Bolt Specification
The ASTM A453 specification covers standards for Grade 660 (Class A, B, C, and D), Grade 651 (Class A and B), Grade 662 (Class A and B), and Grade 665 (Class A and B) of bolting materials, with ten classes of yield strength ranging from 50 to 120 KSI [345 to 827 MPa], for use in high-temperature service such as fasteners, pressure vessels and flanges.
Bolting materials in ASTM A453 are covered rolled, forged, or hot-extruded bars, and also bolts, nuts, screws, washers, studs, and stud bolts.
We offer precisely made Stud Bolts, Hex Bolts, Heavy Hex Bolts, Socket Head Cap Screws, Threaded Rods, Nuts & Washers as per ASTM A453 Grade 600 Class A.
We produce these Grade 660 Class A Bolts from 3/8″ to 4″ in imperial and upto M100 in metric sizes.
Larger size bolts can be made to order as per request. We also undertake custom made boltings in A453 Gr 660 as per drawing. We stock premium and surplus bar stock in Grade 660 (UNS S66286 ; Alloy A286) for quick manufacturing and shorter delivery periods. These ASTM A453 Grade 660 Class A Bolts are supplied with EN 10204 Type 3.1 MTC. We offer Rupture Test Facility for sufficient quantity order.
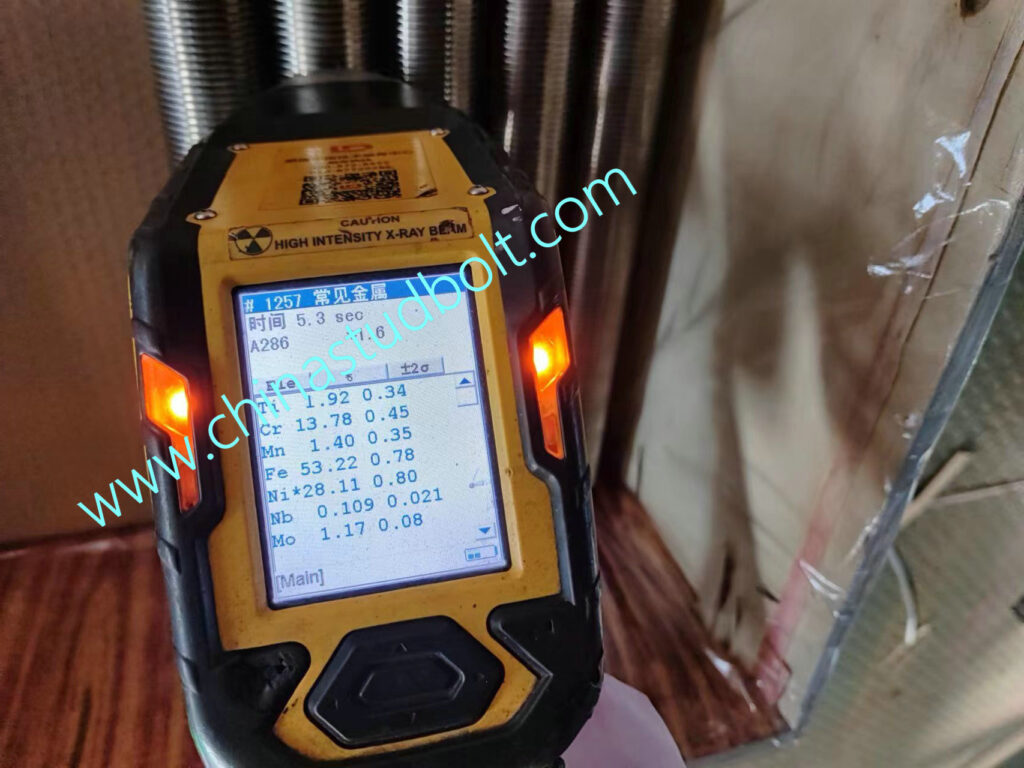
ASTM A453 Grade 660 Chemical Composition (UNS S66286)
Element |
Content % |
|---|---|
| Grade 660 UNS S66286 | |
| Carbon | 0.08 max |
| Manganese | 2.00 max |
| Phosphorus | 0.04 max |
| Sulfur | 0.03 max |
| Silicon | 1.00 max |
| Nickel | 24.00 – 27.00 |
| Chromium | 13.50 – 16.00 |
| Molybdenum | 1.00 – 1.50 |
| Titanium | 1.90 – 2.35 |
| Aluminum | 0.35 max |
| Vanadium | 0.10 – 0.50 |
| Boron | 0.001 – 0.010 |
ASTM A453 Grade 660 Class A/B/C/D STUD BOLT Mechanical Properties
| Grade | Class | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength | Elongation in 4D, min, % |
Reduction of Area, min, % |
Brinell Hardness Number |
Approximate Rockwell Hardness, B & C |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ksi | Mpa | Ksi | Mpa | min | max | |||||
| Grade 660 | A, B and C | 130 | 895 | 85 | 585 | 15 | 18 | 248-341 | 24 HRC | 37 HRC |
| Grade 660 | D | 130 | 895 | 105 | 725 | 15 | 18 | 248-341 | 24 HRC | 35 HRC |
ASTM A453 Grade 660 Class A/B/C/D STUD BOLT Heat Treatment Requirements
| Grade | Class | Solution Treatment | Hardening Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 660 | A | 1650 +/- 25° F [900 +/- 14°C], hold 2 hr, min and liquid quench | 1325 +/- 25° F [720 +/- 14°C], hold 16 hr, air cool |
| Grade 660 | B | 1800 +/- 25° F [980 +/- 14°C], hold 1 hr, min and liquid quench | 1325 +/- 25° F [720 +/- 14°C], hold 16 hr, air cool |
| Grade 660 | C | 1800 +/- 25° F [980 +/- 14°C], hold 1 hr, min and oil quench | 1425 +/- 25° F [775 +/- 14°C], hold 16 hr, air cool, followed by 1200 +/- 25°F [650 +/- 14°C], air cool |
| Grade 660 | D | 1650 +/- 25° F [900 +/- 14°C], hold 2 hr, min and liquid quench 1800 +/- 25° F [980 +/- 14°C], hold 1 hr, min and liquid quench |
1325 +/- 25° F [720 +/- 14°C], hold 16 hr, air cool, If required to achieve properties, second age: 1200 +/- 25°F [650 +/- 14°C], air cool |
ASTM A453 Grade 660 Stud Bolt Applications
Stud bolts made to ASTM A453 Grade 660 are used in:
- Turbine casings in power plants.
- Heat exchangers and boiler systems.
- Pressure vessels in refineries and petrochemical plants.
- Flanged connections in high-temperature environments.
Benefit of ASTM A453 Grade 660
- High Temperature Strength: Excellent mechanical properties up to 700°C (1292°F).
- Corrosion Resistance: Performs well in oxidizing and reducing environments.
- Reliability: Suitable for thermal cycling and prolonged exposure to high stress.
ASTM A453 Grade 660 stud bolts are the right choice for applications requiring exceptional strength and stability in high-temperature and corrosive environments. Selecting the appropriate class (A, B, C, or D) depends on the specific mechanical and environmental requirements of your project.







